Deep contrastive variational subspace clustering
Jul 8, 2025·,,,·
0 min read
Marcos De S. Oliveira
Sergio Ricardo De Melo Queiroz
Cleber Zanchettin
Francisco De Assis Tenório De Carvalho
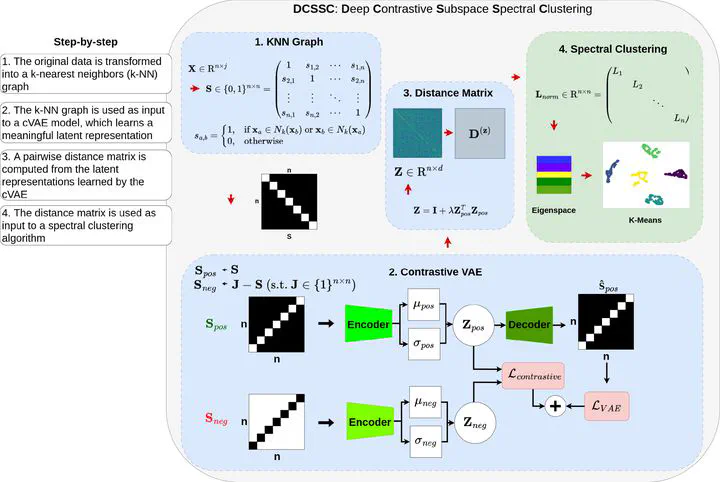
Abstract
Subspace clustering aims to group data points that lie in multiple low-dimensional subspaces within a high-dimensional space. Traditional shallow methods rely on linear optimization and self-expressive properties but struggle with complex, high-dimensional, and limited data samples. In contrast, Deep subspace clustering methods leverage neural networks to learn feature representations, but often specialize in specific domains, such as images, and require extensive training datasets. Furthermore, most approaches rely solely on raw features, making it difficult to capture meaningful structures in data with few examples. To address these challenges, we propose Deep Contrastive and Variational Subspace Spectral Clustering (DCSSC), a novel method that integrates relational information through a similarity matrix, enhancing clustering performance. DCSSC consists of three stages: (1) constructing a neighborhood graph for data representation, (2) training a contrastive variational autoencoder (cVAE) to learn embeddings, and (3) generating an enhanced distance matrix for spectral clustering. Our method is computationally efficient and performs well with minimal training data. Extensive experiments on simulated and 19 real-world datasets from diverse domains, including text, images, and bioinformatics, demonstrate the superiority of DCSSC over state-of-the-art deep and shallow clustering methods. Code is available at https://github.com/marcosd3souza/DCSSC.
Type
Publication
Neurocomputing